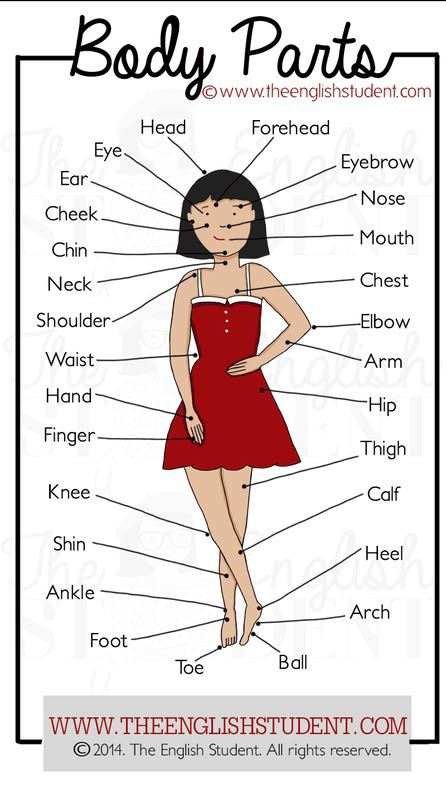
General Knowledge Questions and Answers for Kids (Age Group 4 to 7 years)
1. Which animal is known as the 'Ship of the Desert"?
Ans. Camel
2. How many days are there in a week?
Ans. 7 days
3. How many hours are there in a day?
Ans. 24 hours
4. How many letters are there in the English alphabet?
Ans. 26 letters
5. Rainbow consist of how many colours?
Ans. 7 colours
6. How many days are there in a year?
Ans. 365 days (not a leap year)
7. How many minutes are there in an hour?
Ans. 60 minutes
8. How many seconds are there in a minute?
Ans. 60 seconds
9. How many seconds make one hour?
Ans. 3600 seconds
10. Baby frog is known as.......
Ans. Tadpole
11. How many consonants are there in the English alphabet?
Ans. 21 Consonants
12. How many vowels are there in the English alphabet and name them?
Ans. 5 vowels namely a, e, i, o, and u.
13. Which animal is known as the king of the jungle?
Ans. The Lion is known as the king of the jungle.
14. Name the National bird of India?
Ans. The Peacock
15. Name the National animal of India?
Ans. Tiger
16. What is the National Anthem of India?
Ans. The National Anthem of India is Jana Gana Mana.
17. Name the national flower of India?
Ans. Lotus flower
18. Name the National fruit of India?
Ans. Mango
19. What is the National song of India?
Ans. Vande Mataram
20. Who designed the National Flag of India?
Ans. The flag was designed by Pingali Venkayya.
21. Name the National game of India?
Ans. India does not have an official National Game.
22. Name the National tree of India?
Ans. Banyan tree
23. Name the National river of India?
Ans. Ganga
24. Name the National Reptile of India?
Ans. King Cobra
25. What is the capital of India?
Ans. New Delhi
26. Name the biggest continent in the world?
Ans. Asia
27. How many continents are there in the world?
Ans. 7 continents
28. Name the primary colours?
Ans. Red, Yellow, and Blue
29. Which is the smallest month of the year?
Ans. February
30. Name the house made of ice?
Ans. Igloo
31. Which colour symbolises peace?
Ans. White
32. Name the largest mammal?
Ans. Blue Whale
33. Sun rises in the.....
Ans. East
34. How many sides are there in a triangle?
Ans. Three
35. Name the largest planet of our Solar System?
Ans. Jupiter
General Knowledge Questions and Answers for Kids (Age Group 8 to 10 years)
36. Name the place known as the Roof of the World?
Ans. Tibet
37. Who was the first Prime Minister of India?
Ans. Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru
38. Who is the first woman prime minister of India?
Ans. Indira Gandhi
39. Who is the first citizen of India?
Ans. The President of India
40. How many states are there in India?
Ans. 28 states
41. How many Union Territories are there in India?
Ans. 8 Union Territories
42. How many years are there in one Millenium?
Ans. 1,000 years
43. Name the first man to walk on the Moon?
Ans. Neil Armstrong
44. Name the Oceans of the World?
Ans. The Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic, and the Southern (Antarctic) oceans.
45. Name the densest jungle in the world?
Ans. The Amazon rainforest
46. Which festival is called the festival of colours?
Ans. Holi
47. What is the Isosceles triangle?
Ans. A triangle in which two sides have the same length or two sides are equal.
48. What type of gas is absorbed by plants?
Ans. Carbon Dioxide
49. How many days a February month have in the leap year?
Ans. 29 days
50. Name the longest river on the Earth?
Ans. Nile
51. Name the smallest continent?
Ans. Australia
52. Which is the principal source of energy for the Earth?
Ans Sun
53. Anti-clockwise is it from left or right?
Ans. Left
54. Name the planet nearest to the Earth?
Ans. Mercury
55. Which festival is known as the festival of light?
Ans. Diwali
56. Name a bird that lays the largest eggs?
Ans. Ostrich
57. Which is the National Aquatic Animal of India?
Ans. River Dolphin
58. Name the National Heritage Animal of India?
Ans. Elephant
59. Which is the tallest mountain in the world?
Ans. Mount Everest
60. Who invented Radio?
Ans. Guglielmo Marconi is known as the father of radio.
General Knowledge Questions and Answers for Kids (Age Group 10 to 12 years)
61. Who invented electricity?
Ans. Benjamin Franklin
62. Which continent is known as the ‘Dark’ continent?
Ans. Africa
63. Name the planet known as the Red Planet?
Ans. Mars
64. Who wrote "Malgudi Days"?
Ans. R. K. Narayan
65. Name the National game of the USA?
Ans. Baseball
66. Who invented Watch?
Ans. Peter Henlein
67. Name the largest 'Democracy' of the world?
Ans. India
68. Which is the smallest bone in the human body?
Ans. Stapes (Ear bone)
69. Name the country known as the Land of the Rising Sun?
Ans. Japan
70. How many millimetres are there in a centimetre?
Ans. 10mm
71. Name the hardest substance available on Earth?
Ans. Diamond
72. Name a shape that has ten sides?
Ans. Decagon
73. Name the largest ocean in the World?
Ans. Pacific Ocean
74. Who is the real founder of Microsoft?
Ans. Bill Gates and Paul G. Allen
75. Who gave the theory of Relativity?
Ans. Albert Einstein
76. Who is the Father of our Nation?
Ans. Mahatma Gandhi
77. Who discovered the X-rays first?
Ans. Wilhelm Roentgen
78. Who gave the universal law of gravitation?
Ans. Issac Newton
79. What is a telescope?
Ans. A telescope is an instrument in the shape of a tube with special pieces of glass (lenses) inside it. It makes things that far away appear bigger and nearer.
80. Name a natural satellite of Earth?
Ans. Moon
82. What are Commonwealth Games?
Ans. The Commonwealth Games are a quadrennial international multi-sport event among the athletes of the Commonwealth Games.
83. How many years of Independence India celebrated on August 15, 2022?
Ans. India celebrated 75 years of Independence on August 15, 2022.
84. How many medals India won in the Commonwealth Games 2022?
Ans. India won total 61 medals in Commonwealth Games 2022.
85. What is the smallest country in the world by land area?
Ans. Vatican City.
86. Who discovered penicillin?
Ans. Alexander Fleming.
87. What is Japan's currency?
Ans. Yen.
88. In which year did the Titanic sink?
Ans. 1912.
89. What is the hardest natural substance on Earth?
Ans. Diamond.
90. Which is the longest river in South America?
Ans. The Amazon River.
91. Who is known as the "Father of Modern Physics"?
Ans. Albert Einstein.
92. What is the largest organ in the human body?
Ans. The skin.
93. What is the capital of Japan?
Ans. Tokyo
94. What is the capital of Germany?
Ans. Berlin
95. What is the capital of Canada?
Ans. Ottawa
96. What is the capital of Russia?
Ans. Moscow
97. What is the capital of the United Kingdom?
Ans. London
98. What is the capital of Mexico?
Ans. Mexico City
99. What is the capital of China?
Answer: Beijing
100. What is the capital of Greece?
Ans. Athens
101. What is the capital of Egypt?
Ans. Cairo
102. What is the capital of Australia?
Ans. Canberra
104. What is the capital of South Africa?
Ans. Pretoria (administrative), Bloemfontein (judicial), Cape Town (legislative)
105. What is the name of the famous clock tower in London?
Ans. Big Ben
106. What is the boiling point of water?
Ans. 100 degrees Celsius
107. What is the currency of the United States?
Ans. Dollar
108. What is the main ingredient in bread?
Ans. Flour
109. What is the main ingredient in chocolate?
Ans. Cocoa
110.What is the main source of energy for the Earth?
Ans. The Sun
111. What do bees produce?
Ans. Honey
112.What is the hardest substance available on Earth?
Ans. Diamond (appears twice in the first list)
113. What is the chemical symbol for water?
Ans. H2O
114. What is the smallest planet in our solar system?
Ans. Mercury
115. Who painted the Mona Lisa?
Ans. Leonardo da Vinci
116. Who is the founder of Microsoft?
Ans. Bill Gates and Paul G. Allen
117. Who is known as the Father of Medicine?
Ans. Hippocrates
118. Who proposed the theory of relativity?
Ans. Albert Einstein
119. Who discovered X-rays?
Ans. Wilhelm Roentgen
120. Who formulated the universal law of gravitation?
Ans. Isaac Newton
121. Who invented the light bulb?
Ans. Thomas Edison
122. Who invented the watch?
Ans. Peter Henlein
123. Which animal is known as the "King of the Jungle"?
Ans. Lion (appears twice in the first list)
124. Which animal is known for its intelligence and ability to use tools?
Ans. Chimpanzee
125. Which animal is known for its long neck?
Ans. Giraffe
126. Which animal is known for its ability to change colors?
Ans. Chameleon
127. Which bird lays the largest eggs?
Ans. Ostrich
128. Which is the tallest mountain in the world?
Ans. Mount Everest
129. Which is the largest bird in the world?
Ans. Ostrich
130. Which is the largest mammal in the world?
Ans. Blue whale
131. Which is the largest land animal?
Ans. African elephant
General Knowledge Questions and Answers for Kids (True or False)
132. 34 teeth in total adults have.
Ans. False (The adult has 32 teeth in total).
133. A barometer is used to measure Atmospheric Pressure.
Ans. True
134. Valentina Tereshkova was the first woman to go into space.
Ans. True
135. Sparrow is a bird known for its intelligence.
Ans. False (Owl is known for its intelligence).
136. Europe is the second smallest continent and the third most populous continent
Ans. True
137. Bosnia and Herzegovina's largest city and capital is Sarajevo.
Ans. True
138. Plants absorbs Oxygen?
Ans. False (Plants absorbs Carbon Dioxide).
139. Denmark's capital and most populous city is Copenhagen
Ans. True
140. Half of 250 is 125.
Ans. True
141. Metre per second is the unit of Speed.
Ans. True
142. William Shakespeare is a scientist.
Ans. False (William Shakespeare was an English dramatist, poet, and actor).
143. There are 200 bones in the Human Body.
Ans. False (206 bones are there in Human Body).
145. Electrons are larger than molecules.
Ans. False
146. With the help of Photosynthesis plants make their own food.
Ans. True
147. Chemical formulae of Hydrochloric acid is HCl.
Ans. True
148. There are 11 players in a cricket team.
Ans. True
149. In 1916 Olympic Games were cancelled because of World War I?
Ans. True
150. In Football, the term Hat-Trick is used.
Ans. False ( The term Hat-Trick is used in cricket).
151. There are nine players in one team of Kho Kho.
Ans. True
152. Commonwealth Games are held every four years.
Ans. True
153. A rainbow has five colours.
Ans. False (Rainbow has 7 colours, VIBGYOR)
154. The main function of the xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves.
Ans. True
155. World Turtle Day is observed on May 23 annually.
Ans. True
156. India is a democratic country?
Ans. True
157. World Cup is held after every 3 years.
Ans. False
158. Tiger belongs to the family of cats.
Ans. True
159. What is the largest planet in our solar system?
Ans. Jupiter
160. What is a shooting star?
Ans. A comet entering Earth's atmosphere
161. Which planet is known for its beautiful rings?
Ans. Saturn
162. What causes the phases of the Moon?
Ans. Sun's Light
163. What is the name of the closest star to Earth?
Ans. Sun
164. What is the launch date for Chandrayaan 3 mission?
Ans. July 14, 2023
165. What is the mission of Chandrayaan 3?
Ans. To demonstrate a safe and soft landing on the lunar surface.
166. Is Chandrayaan-3 a follow up mission of Chandrayaan-2?
Ans. True